DeFi vs CeFi: Introduction
Blockchain technology has generated a whole ecosystem centered around Bitcoin and other digital currencies. Decentralized alternatives will eventually displace traditional financial services, according to a growing body of opinion worldwide. Only time will tell if that will materialize, but we can already see a dynamic rivalry developing within the blockchain ecosystem. Decentralized vs Centralised or “DeFi vs CeFi cryptocurrency conflict.”
Since customers are frequently unaware of the underlying laws or agreements regulating financial assets and goods, the traditional centralized finance (CeFi) environment may need to be clarified to non-experts.
The underlying integrity-protected blockchain of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is helping the ecosystem make a name for itself as one that wants transparency and control. DeFi platforms also claim to offer higher financial asset yields than CeFi platforms. The distinction between CeFi and DeFi might only sometimes be apparent, however.
This article compares and contrasts DeFi vs CeFi in terms of law, security, economy, privacy, and market manipulation.
Overview Of DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
DeFi is an open, international financial system that increases accessibility and transparency in the blockchain industry. Businesses can self-manage various services with DeFi, including trading, insurance, lending, money issuance, staking, payments, financial data, over-the-counter (OTC) trading, asset management, and more.
Banks and other financial institutions that charge usage fees are eliminated with DeFi. Users can store money in a safe digital wallet and transfer money quickly with DeFi, which requires an internet connection. Peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a middleman are made possible by DeFi cryptos.
Top Features Of DeFi
- Quick Innovation: Due to its relentless drive to innovate, the DeFi market has evolved into a rich ecosystem with cutting-edge financial services. DeFi space has been attempting to give alternatives to the problem in functionalities where centralized financial services have developed.
- Trustless: By reviewing their code and using third-party tools like Etherscan to determine whether a transaction was adequately executed, users may confirm that DeFi services operate as intended.
- Permissionless: DeFi does not require authorization because it is decentralized. In contrast, CeFi requires customers to go through a KYC process to access services, which requires them to either deposit money or give personal information.
Overview Of CeFi (Centralized Finance)
CeFi stands for centralized and managed exchanges, wallets, and other financial services. CeFi, or centralized finance, refers to giving money to centralized businesses, such as cryptocurrency exchange platforms, to store and administer. Users have an alternative to conventional banking goods and services via CeFi.
Users can store, transmit, and receive money using CeFi crypto services without the aid of a bank or other financial institution. The blockchain, a distributed ledger technology that provides secure, transparent, and immutable transaction data, is still the foundation for constructing CeFi services. CeFi services are accessible to everyone with an internet connection and a digital device, unlike traditional banking services.
Top Features Of CeFi
- Flexibility Of Fiat Conversion: Centralized services are a more proper handshake for the transfer in light of the current changes, where the Web2 ecosystem is adapting to comply with Web3 space requirements. When converting fiat currency to cryptocurrency and vice versa, CeFi offers greater freedom than decentralized services. Typically, a centralized company is needed for this capability of converting between cryptocurrency and money.
- Cross-Chain Services: Unlike DeFi, CeFi services can facilitate the trade of on-chain coins like LTC, XRP, BTC, and other tokens frequently created on independent blockchain platforms. DeFi services do not support these tokens, and they have not yet been able to overcome the smoothness of the activity due to the latency and complexity of completing cross-chain exchanges. CeFi can solve this problem by obtaining custody of money from several chains.
- Centralized Exchange (CEX): These are conventional crypto exchanges where customers send money to the exchange and manage it through an internal account. As useful as this characteristic is for the constantly changing crypto industry, it has also made centralized exchanges the focus of numerous incidents in recent years.
DeFi vs CeFi: Examples
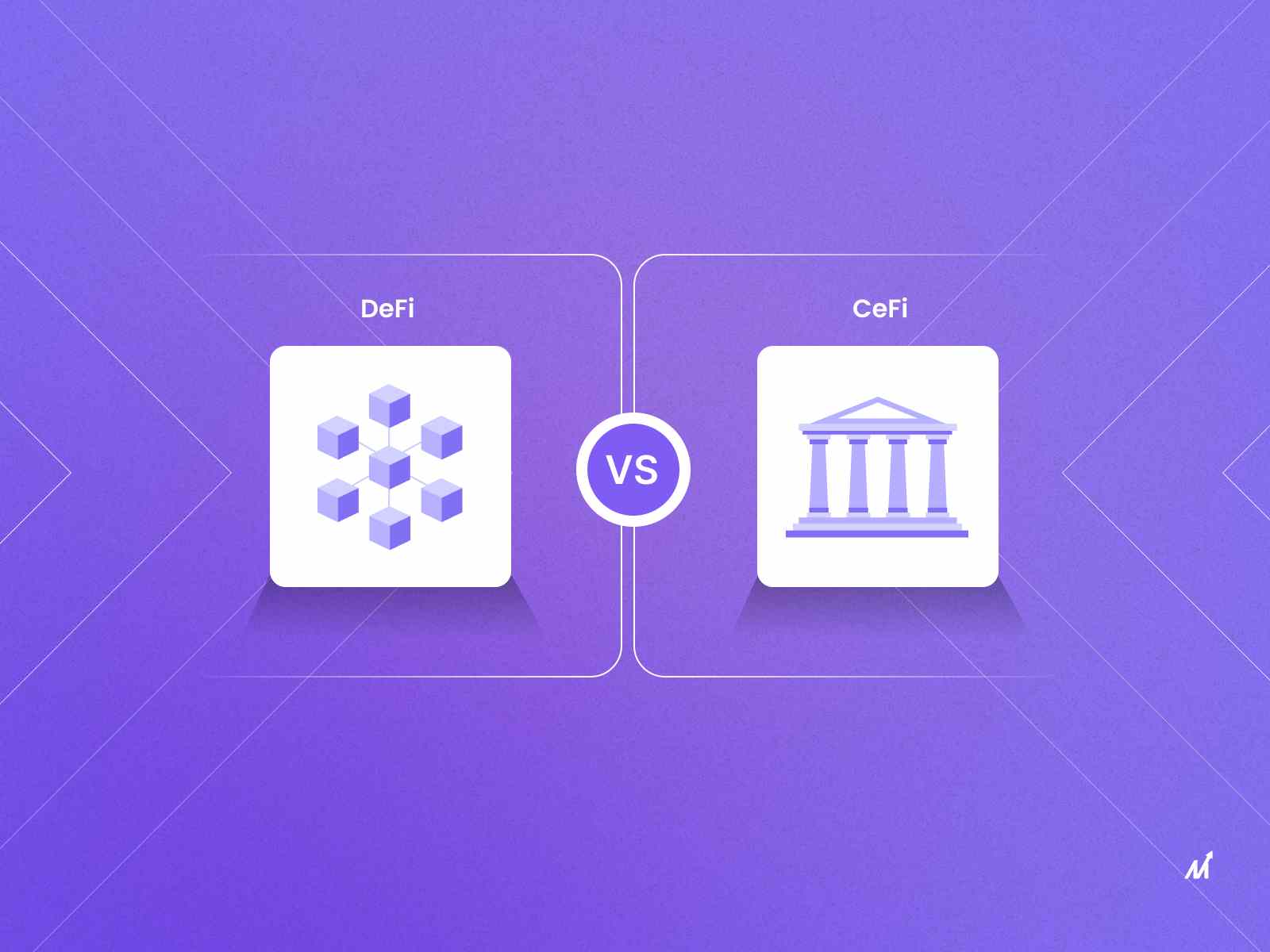
DeFi Examples
- Kyber: A decentralized marketplace
- MakerDAO: A decentralized device for stablecoin minting and lending
- bZx: It is a decentralized platform for lending and margin trading
- Totle: It is a decentralized liquidity aggregator that automatically optimizes prices
- Augur: A decentralized predictions market exists here
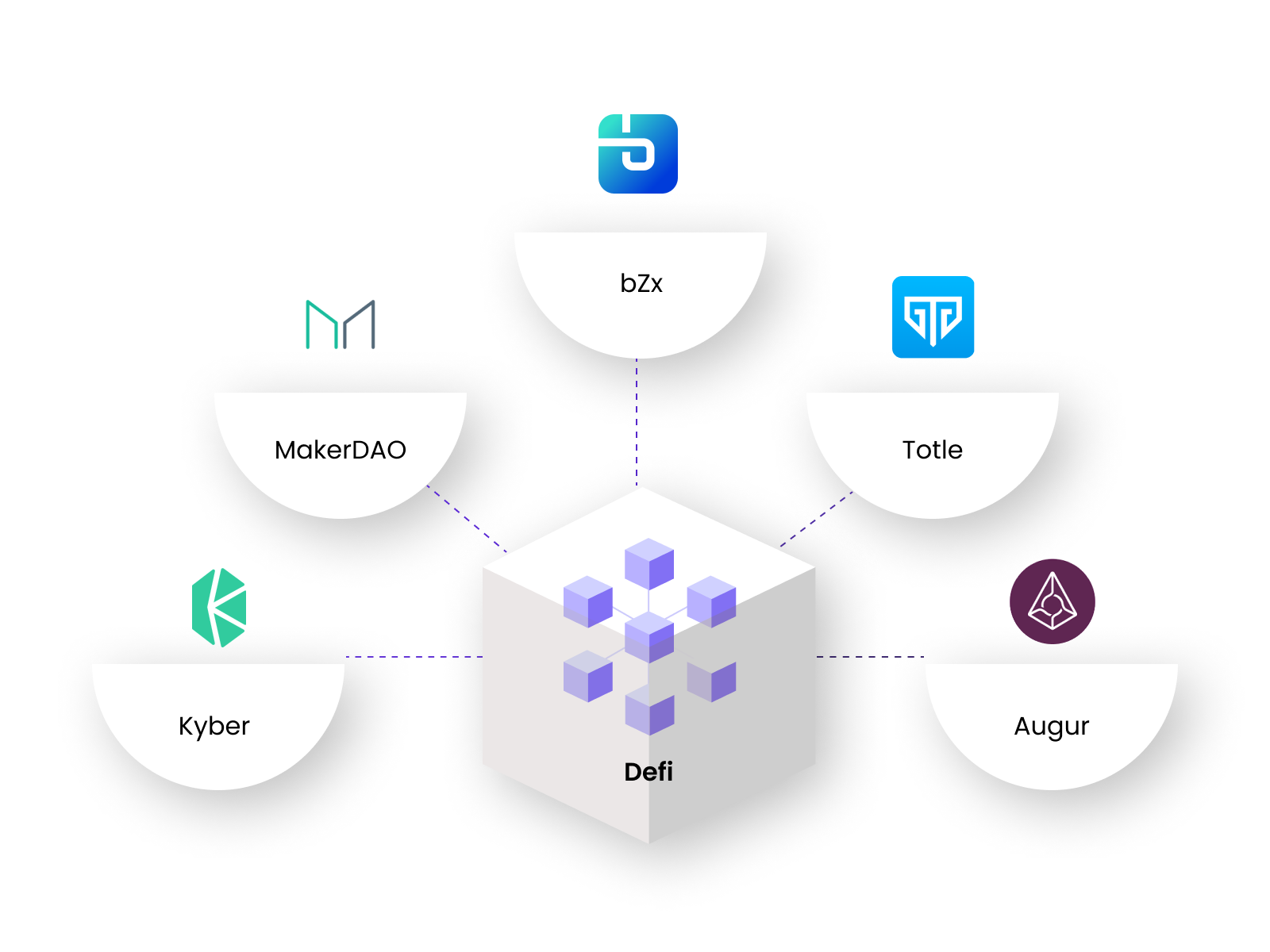
CeFi Examples
- Celsius: A cryptocurrency lending and borrowing platform
- Ledn: A platform for borrowing and lending that works with DAI to guarantee Bitcoin
- Libra: It is a global cryptocurrency layer and financial system
- Coinbase: An exchange for cryptocurrencies that makes it easier to trade, borrow, use margin, use native stablecoins, lend money, make payments, and more
- BlockFi: It is a platform for lending and borrowing in cash and cryptocurrencies
DeFi vs CeFi: Pros & Cons Explored
Pros Of DeFi
- Anonymity: Because no personal information is necessary and the DeFi user’s wallet is unrelated to their real identity, they can enjoy anonymity.
- Unrestricted: Anyone with a wallet and an internet connection can use DeFi products. There aren’t any limitations.
- Self-custody: Because they control the private keys, cryptocurrency users are in charge of their possessions. Therefore, nobody can prevent them from accessing their money.
- Transparent: The public may view DeFi transactions on the blockchain. For users, this fosters transparency.
Cons Of DeFi
- Scalability: The blockchains on which DeFi protocols are based are essential to their operation. As a result, they inherit the scalability problems associated with these blockchain networks. Low transaction throughputs, which result in high transaction costs when the network is crowded, are one example of a scalability problem.
- The Risk Associated With Smart Contracts: Thieves may use the smart contract’s flaws to steal digital assets secured by the DeFi protocol. The learning curve is steep since DeFi protocols are novel and unorthodox. Beginners could therefore find them challenging to utilize or comprehend. This means that before engaging with DeFi and its goods, individuals must take their time to learn them.
Pros Of CeFi
- Fiat-To-Crypto Assistance: Users can easily purchase cryptocurrency with their local currency on a centralized cryptocurrency exchange. Depending on the country in which they operate, CEXs accept numerous fiat currencies.
- Common: CeFi platforms function similarly to established financial service providers. They will therefore be quite simple to use and familiar to most people.
Cons Of CeFi
- Lack Of Sheer: CeFi businesses make decisions in secret. Users might need to be made aware of their trading methods. Additionally, because of their off-chain technologies, the exchange’s transactions are not added to the blockchain.
- Constrictive: Due to possible location restrictions, CEXs may not be accessible to everyone. For instance, certain exchanges might not permit traders from particular (black-listed) nations to use their platform. Regulations may require the implementation of sure of these restrictions.
- Custodial: Since CEXs own their users’ private keys, they are in charge of the digital assets in their users’ wallets and accounts. If the site stops accepting deposits and withdrawals, users may only be able to access their holdings with these private keys.
- Personal Information Is Necessary: Users must be willing to reveal their personal information, including names, residence addresses, data from their national identification cards, and selfie images, to utilize CEXs.
DeFi vs CeFi: Properties Compared
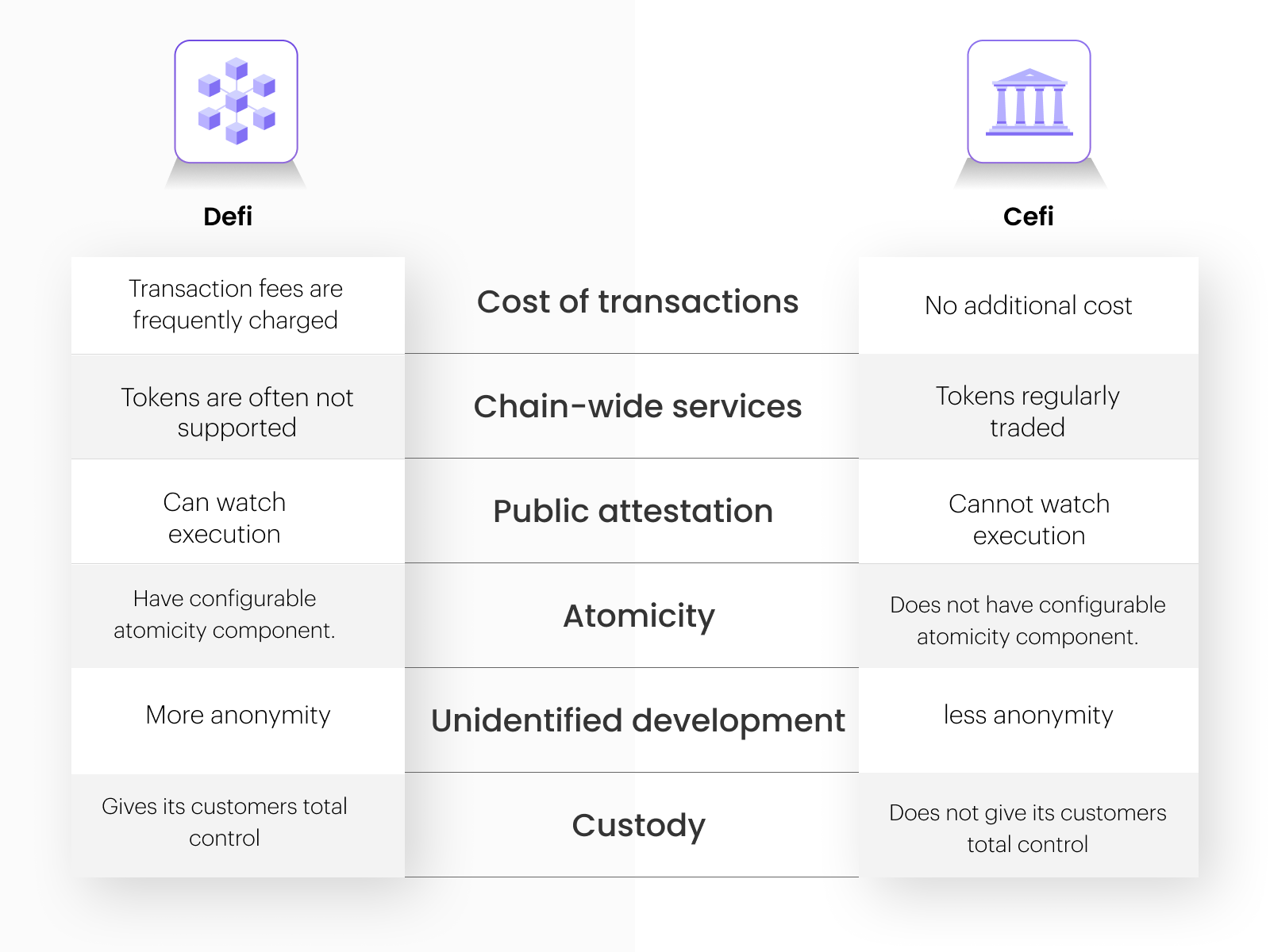
1. Cost Of Transactions
Transaction fees are frequently charged in DeFi. The institutions in CeFi, on the other hand, provide transactions at no additional cost because CeFi conducts stringent KYC and AML checks.
2. Cross-Chain Services
Trading BTC and other valuable coins developed on various blockchains frequently use CeFi services. Due to the difficulty and duration of atomic cross-chain trades, DeFi services often do not handle these coins.
CeFi services take care of this problem by keeping cash from numerous chains (whereas decentralized services require that tokens follow Ethereum token standards to achieve interoperability). This is a significant benefit for CeFi as many currencies with the greatest market caps and active trading volumes are spread across many blockchains and do not adhere to interoperability standards.
3. Public Attestation
While the underlying DeFi application code might not always be open-source, non-custodial DeFi must have publicly verifiable execution and bytecode on a blockchain. Therefore, unlike CeFi, any DeFi user may see and confirm that DeFi state changes are carried out correctly. The new DeFi technology has an unmatched ability to transfer trust because of this transparency.
4. Atomicity
A blockchain transaction enables the execution of subsequent actions, which may include several financial transactions. It is possible to make this combination atomic, which means that all of the operations in the transaction will either succeed or fail simultaneously. Although CeFi lacks this programmable atomicity quality, atomicity in CeFi may nevertheless be enforced through pricey and time-consuming legal agreements.
5. Unidentified Development & Deployment
Less privacy is offered to users by centralized finance than by DeFi transactions. Even Bitcoin’s creator has remained a mystery up to this point, and many DeFi initiatives are developed and run by anonymous teams. Once implemented, the DeFi smart contracts are implicitly run by the miners. Unknown DeFi applications can operate without a front-end, forcing users to interact with the smart contract directly.
6. Custody
DeFi, unlike CeFi, enables users to instantly control their assets (there is no need to wait for the bank to open). But with immense power also comes great responsibility. Users bear the majority of technology risks unless such insurance is insured. As a result, holding bitcoin assets is particularly common with centralized exchanges, which are essentially the same as conventional custodians.
Quick Comparison
| Aspect | DeFi (Decentralized Finance) | CeFi (Centralized Finance) |
| Control | Operates on a decentralized network, typically using blockchain technology. Users have full control over their assets. | Controlled by centralized institutions (banks, financial firms). Users entrust assets to these entities. |
| Access and Inclusion | Accessible to anyone with an internet connection, enhancing financial inclusion, especially for unbanked populations. | Requires traditional banking systems, often with geographical or financial barriers to access. |
| Transparency | High transparency due to the blockchain’s public ledger. All transactions are visible and verifiable by anyone. | Limited transparency; operations are often not disclosed to the public. |
| Security | Relies on cryptographic security and smart contract protocols. Vulnerable to smart contract bugs and hacking. | Security is managed by the institution, with established protocols and insurances, but subject to internal fraud and cyber-attacks. |
| Regulation | Generally operates in a regulatory grey area. Subject to evolving regulations. | Highly regulated with strict compliance requirements (KYC, AML, etc.). |
| Intermediaries | Eliminates traditional intermediaries using smart contracts and decentralized protocols. | Involves intermediaries like banks, brokers, and agents. |
| Transaction Speed | Can vary depending on the blockchain used. Some networks offer faster transactions than others. | Typically fast but can be delayed due to institutional processes. |
| Fees | Variable fees depending on network congestion and transaction complexity. Potentially lower than CeFi for some operations. | Fees set by the institution, including service charges, account fees, etc. |
| Asset Ownership | Users hold their assets in personal wallets, retaining direct ownership. | Assets are held by the institution; users have indirect ownership. |
| Interest Rates | Often offers higher interest rates for savings and lending due to the elimination of intermediaries and operational efficiencies. | Interest rates are generally lower, influenced by central bank policies and institutional costs. |
| User Experience | Can be complex and intimidating for beginners. Requires understanding of wallets, tokens, and blockchain technology. | User-friendly interfaces with customer support. Easier for the general public to understand and use. |
| Financial Products | Innovative and diverse, including yield farming, liquidity pools, and synthetic assets. Still evolving. | Traditional products like loans, savings accounts, and investment services. More standardized. |
| Risk and Volatility | Higher risk and volatility, partly due to the nascent and speculative nature of the market. | Generally perceived as safer with established risk management practices. |
| Interoperability | High interoperability within the blockchain and DeFi ecosystems. Seamless interaction between different DeFi services. | Limited interoperability; often confined within the institution’s or partners’ ecosystem. |
| Recovery and Support | Limited recourse in case of errors or loss (e.g., sending funds to the wrong address). No customer support. | Institutional support available for disputes and errors, with potential for asset recovery. |
| Scalability | Scalability can be an issue on some blockchains, impacting transaction costs and speeds. | Established infrastructure capable of handling large volumes of transactions efficiently. |
| Anonymity and Privacy | Offers greater anonymity, with no requirement for personal information for transactions. Privacy varies by blockchain. | Requires personal information for account creation and transactions, impacting privacy. |
DeFi vs CeFi: Synergies
The DeFi market is still in its infancy. Due to the blockchain settlement layer, DeFi shares specific characteristics with CeFi, such as transparency, non-custody, and decentralization. The blockchain offers numerous benefits but has limitations regarding transaction throughput, confirmation delay, and privacy for DeFi. DeFi still has a strong reliance on the conventional banking system, nevertheless. More specifically, on DeFi, the value of crypto assets is still principally established and acknowledged in fiat money.
CeFi steps in at this point. The CeFi lending platforms link the established financial system and the cryptocurrency asset market. More crucially, DeFi and CeFi share a common objective. In addition to driving the economy, both sectors strive to offer consumers high-quality financial products and services. In conclusion, there is no simple solution to integrate the finest aspects of both systems, and both DeFi and CeFi have their own unique set of advantages and disadvantages.
Therefore, it will be necessary for both of these distinct but linked financial systems to coexist and mutually benefit. DeFi and Cefi have a few synergistic opportunities to offer one another.
DeFi vs CeFi: Which One Is Used By More Businesses?
CeFi guarantees the safety of money and honest dealing with it. Trading in cryptocurrencies is also open to investors using traditional currencies. They also receive customer support services from CeFi exchanges that DeFi services do not. DeFi, on the other hand, wishes to keep the area free of intrusion. It gives investors a place to put their plans into practice without working through an intermediary.
Both models have advantages and disadvantages, according to the investor’s requirements. DeFi is the best model to select if privacy and openness are essential to users. On the other hand, users should use CeFi if their top priorities are trust, sharing risks, flexibility, and more investment possibilities.
Markovate’s Take: Which Is Better?
Since both financial solutions have pros and disadvantages, it is impossible to say which is preferable. In the end, everything relies on the requirements of various users. For example, individuals who highly emphasize financial independence and privacy may opt for DeFi protocols, but institutional investors frequently favor regulated CeFi platforms. This may be the reason CeFi vs DeFi has coexisted for so long.
Theoretically, decentralized finance is preferable to centralized finance for cryptocurrency investors. The DeFi market has yet to develop to the point where investors may use it with confidence.
DeFi vs CeFi: Commonly Asked Questions
1. Is Bitcoin a CeFi or DeFi?
Through CeFi services, trades in Bitcoin and other popular currencies created on independent blockchains often happen. DeFi services usually do not handle these tokens since atomic cross-chain transactions are complex and time-consuming.
2. Is DeFi better than CeFi for enterprises?
Decentralized finance is a fundamental principle of cryptocurrencies, yet DeFi systems might be challenging to use initially. Centralized financial platforms may offer users a more exact and recognizable point of entry.
3. Which model should I choose to start my business?
DeFi is easier to use than CeFi. As a result, users cannot invest, borrow, or lend money through the conventional financial system. With DeFi, users would be required to begin supporting their money with an internet connection, some knowledge of cryptocurrency, and a basic comprehension of DeFi.

I’m Rajeev Sharma, Co-Founder and CEO of Markovate, an innovative digital product development firm with a focus on AI and Machine Learning. With over a decade in the field, I’ve led key projects for major players like AT&T and IBM, specializing in mobile app development, UX design, and end-to-end product creation. Armed with a Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Science and Scrum Alliance certifications, I continue to drive technological excellence in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.